How to Calculate Conduit Wire Fill 2026 | Northern Colorado, Fort Collins & Greeley
In 2026, conduit wire fill in Northern Colorado must comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) and local Larimer and Weld County standards. For residential projects in Fort Collins, Greeley, and Loveland, the 40% fill rule for three or more conductors ensures proper heat dissipation and safety.
Conduit wire fill refers to how much of a conduit’s internal cross-sectional area is occupied by insulated wires or cables.
The National Electrical Code (NEC) limits the amount of wire you can safely run inside a conduit to prevent:
- Overheating & insulation damage
- Voltage drop
- Difficult wire pulls
- Safety hazards & fire risk
- NEC code violations
- Premature conductor failure
Improper conduit fill is one of the top causes of failed inspections and wiring malfunctions.
This guide shows how to calculate conduit fill step-by-step and includes charts, formulas, and NEC-compliant examples.
NEC Conduit Fill Percentages (What the Code Allows)
According to the NEC:
Number of Conductors, Maximum Fill %1 conductor, 53% 2 conductors, 31% 3+ conductors 40%
40% is the most common number used in real installations because most conduit runs contain at least three conductors (hot, neutral, ground).
2026 Northern Colorado Conduit Fill Standards
In the Front Range, local municipalities have specific nuances for residential conduit installations:
- Fort Collins & Loveland: These cities follow strict NEC Chapter 9 tables. If you are running conduit for a basement finish or a detached garage, the Pikes Peak Regional Building Department (PPRBD) standards—often used as a benchmark—require a rough-in inspection before any conduit is concealed.
- Greeley & Weld County: For underground conduit (common for outdoor lighting or hot tubs), the top of the conduit must be buried at least 18 inches deep.
- The 60% Nipple Rule: For short runs of 24 inches or less between panels or boxes in Severance or Eaton homes, the NEC allows a higher 60% fill capacity. Weld County (.gov)
2026 NEC Conduit Fill Quick-Reference Table
Number of Conductors Maximum Allowable Fill (%)Application Note
1 -Conductor 53% Typically used for single large service cables.
2 -Conductors 31% Lower fill due to the "Figure-8" shape of two wires.
3- Conductors 40% The standard "40% Rule" for most NOCO residential circuits.
4-Conduit Nipple 60% Applies only to raceways 24 inches or shorter.

This method works for EMT, PVC, IMC, Rigid Metal Conduit (RMC), FMC, LFNC, ENT, and more.
Step 1: Identify the Conduit’s Internal Area
Look up the internal cross-sectional area of your conduit’s trade size.
(Example: ¾" EMT has an area of 0.533 in²)
Step 2: Determine Wire Area (per Conductor)
Use NEC Chapter 9, Table 5 (or manufacturer specs).
Example: 12 AWG THHN = 0.0133 in² per conductor
Step 3: Multiply Wire Area × Number of Conductors
Example:
3 × 12 AWG THHN =
0.0133 × 3 = 0.0399 in² total wire area
Step 4: Calculate Percentage Fill
Formula:
Fill % = (Total Wire Area ÷ Conduit Area) × 100
Example:
0.0399 ÷ 0.533 = 7.48% fill
Step 5: Compare Against NEC Limits
If your fill percentage is 40% or below, you’re compliant for 3+ conductors.
If above → increase conduit size or reduce wire quantity/gauge.
Conduit Fill Quick Chart (Most Common Electrician Reference Values)
Use the following as a quick estimator (always confirm with NEC tables):
How Many Wires Fit in ¾" EMT?
Wire Gauge Approx. Max Conductors
14 AWG THHN - 27
12 AWG THHN - 21
10 AWG THHN - 14
8 AWG THHN - 9
6 AWG THHN - 5
These errors cause inspections to fail or lead to overheating:
❌ Forgetting to Count the Ground Wire
Ground conductors do count toward fill calculations.
❌ Mixing Wire Types Without Adjustment
Different manufacturers = different diameters.
THHN ≠ XHHW ≠ NM cable ≠ Control cable.
❌ Using Wire Count Instead of Cross-Sectional Area
NEC requires area-based calculation — not “how many wires fit.”
❌ Ignoring Long Runs or Multiple 90° Bends
More bends = higher pulling tension = need for larger conduit.
❌ Not Planning for Future Expansion
Always oversize conduits when possible.
Follow these guidelines to ensure safe, trouble-free installations:
- Use a minimum of 40% fill for 3+ conductors
- Oversize conduit on long runs
- Keep bend count low (no more than 360° total between pull points)
- Separate high-voltage and low-voltage cables
- Avoid mixing THHN, NM, and armored cable types
- Use lube for long pulls or larger gauge conductors
EMT (Electrical Metallic Tubing)
Most common for residential & commercial; smooth interior for easy pulls.
PVC Conduit
Significant for underground runs; interior friction slightly higher.
RMC / IMC
Industrial-grade, thicker wall; may require upsizing due to heavy fittings.
Flexible Conduit (FMC, LFNC)
Friction is high — derate or upsize by one trade size.
Proper wire fill ensures:
- Reduced heat buildup
- Longer wire lifespan
- Smoother wire pulls
- Lower voltage drop
- NEC inspection compliance
- Lower fire risk
It’s one of the most overlooked but critical parts of any safe electrical installation.
Consider hiring a professional if:
- You’re running multiple circuits in one conduit
- You’re unsure how to follow NEC requirements
- You’re installing in commercial/industrial settings
- You’re mixing wire types (low voltage + high voltage)
- Your installation has more than 2 bends
AC/DC Electric can help ensure the installation is safe, compliant, and long-lasting.
Understanding conduit fill calculations
Regarding electrical installations, accurate wire fill calculation is important.
for ensuring the safety and efficiency of the system. Conduit fill calculations help determine the maximum number of wires an electrician can safely install in a conduit based on its size and the diameter of the wires. These calculations prevent overheating, voltage drop, and other potential hazards.
Understanding conduit fill calculations is essential to grasp the concept of "fill ratio." The fill ratio refers to the percentage of the conduit's cross-sectional area occupied by the wires. The fill ratio must not exceed the allowable limit specified by electrical codes to maintain proper airflow and prevent excessive heat buildup. By calculating the fill ratio, you can determine the appropriate conduit size for a given number and size of wires.
Importance of Accurate Wire Fill Calculation
Accurate wire fill calculation is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures compliance with electrical codes and regulations. These codes have been designed to prioritize safety and prevent potential hazards. By accurately calculating the wire fill, so you can make sure that your electrical installation meets the required standards.
Additionally, accurate wire fill calculation promotes efficiency. Overcrowded conduits can impede airflow and cause excessive hot temperature buildup, leading to premature wear and tear on wires, insulation, and other components. By calculating the wire fill accurately, you can optimize the conduit size, allowing for proper ventilation and reducing the risk of overheating.
Furthermore, accurate wire fill calculation helps prevent voltage drop. When too many wires are packed tightly in a conduit, it can lead to increased resistance and voltage drop, affecting the electrical system's performance. By calculating the wire fill accurately, you can ensure that the current-carrying capacity of the wires is not compromised, maintaining a stable voltage supply.
Standard terms used in conduit fill calculations
Before diving into the details of conduit fill calculation, it's essential to familiarize yourself with some standard terms used in this process:
- Conduit: A conduit is a pipe or tube that protects and routes electrical wires.
- Wire Diameter: Refers to size and the diameter of the individual wires being installed in the conduit.
- Conduit Fill Ratio: The percentage of the conduit's cross-sectional area occupied by the wires.
- Conduit Fill Capacity: Most wires can be installed safely in a conduit.
- Conduit Fill Chart: A graphic representation of conduit sizes and their corresponding fill capacities.
- NEC: The National Electrical Code is a set of standards and regulations governing electrical installations in the United States.
Now that we have a basic understanding of the terms involved in conduit fill calculations let's explore the tools that can help simplify this process and ensure accuracy.
The Conduit Fill Calculator: How it works
The Conduit Fill Calculator is a powerful tool simplifying calculating wire fill in conduits. This online calculator considers various factors such as conduit size, wire diameter, and number of wires to provide accurate results.
To use the Conduit Fill Calculator effectively, you must gather information beforehand. Start by determining the size of the conduit and the diameter of the wires you intend to install. Then, enter these values into the calculator along with other relevant details, such as the type of conduit material and the ambient temperature.
Once you have entered all the required information, the Conduit Fill Calculator will generate the maximum fill capacity of the conduit, expressed as a percentage. This calculation will help you determine whether the selected conduit size is appropriate for the number and size of wires you plan to install. The Conduit Fill Calculator replaces the need for calculations to be done manually, reducing the chances of errors and ensuring accurate results.
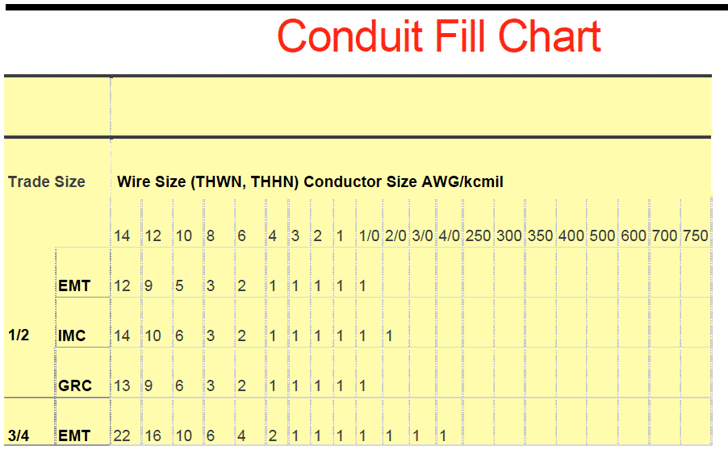
Conduit Fill Chart for Accurate Calculations
The Conduit Fill Chart is another valuable tool that complements the Conduit Fill Calculator. This chart visually represents different conduit sizes and their corresponding fill capacities. It is beneficial when you want to quickly determine the appropriate conduit size without performing complex calculations.
To use the Conduit Fill Chart effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the size of the conduit you plan to use.
- Determine the diameter of the wires you intend to install.
- Locate the conduit size on the chart and find the corresponding wire size column.
- Find the intersection of the conduit and wire size to determine the maximum fill capacity expressed as a percentage.
You can cross-check your calculations and ensure accurate results by using the Conduit Fill Chart in conjunction with the Conduit Fill Calculator. These tools provide a comprehensive solution for efficient and precise wire fill calculation.
Cat 6 Conduit Fill Chart
When it comes to specific types of wires, such as Cat 6 cables, it's essential to use the appropriate conduit fill chart to ensure accurate calculations. The Cat 6 Conduit Fill Chart specifically addresses the wire fill requirements for Cat 6 cables, commonly used for high-speed data transmission.
To use the Cat 6 Conduit Fill Chart effectively, follow these steps:
- Determine the size of the conduit and the diameter of the Cat 6 cables.
- Locate the conduit size on the chart and find the corresponding Cat 6 wire size column.
- Find the intersection of the conduit and wire size to determine the maximum fill capacity expressed as a percentage.
Following this guide, you can make accurate wire fill calculations for Cat 6 cables, ensuring optimal performance and compliance with industry standards.
NEC Conduit Fill Table for different types of Conduits
The NEC Conduit Fill Table is a comprehensive resource that provides detailed information on wire fill requirements for various types of conduit. This table is based on the guidelines neccesary by the National Electrical Code (NEC), ensuring compliance with industry standards.
To use the NEC Conduit Fill Table effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the type of conduit you plan to use, such as EMT, PVC, or rigid metal.
- Determine the size of the conduit and the diameter of the wires you intend to install.
- Locate the conduit type and size on the table.
- Find the corresponding wire size column and determine the maximum fill capacity expressed as a percentage.
The NEC Conduit Fill Table provides a comprehensive reference for wire fill calculations, ensuring safe and compliant electrical installations.

PVC Conduit Fill Chart
PVC conduit is a in demand choice for electrical installations due to its durability, flexibility, and ease of installation. To ensure accurate wire fill calculations for PVC conduit, utilizing the PVC Conduit Fill Chart is essential.
To use the PVC Conduit Fill Chart effectively, follow these steps:
- Determine the size of the PVC conduit and the diameter of the wires you plan to install.
- Locate the conduit size on the chart and find the corresponding wire size column.
- Find the intersection of the conduit and wire size to determine the maximum fill capacity expressed as a percentage.
Utilizing the PVC Conduit Fill Chart ensures proper wire fill calculations for PVC conduit, promoting safe and efficient electrical installations.
Southwire Conduit Fill: What you need to know
Southwire is a leading manufacturer of electrical wire and cable products, and they offer a comprehensive conduit fill guide to assist professionals in accurate wire fill calculations. The Southwire Conduit Fill guide provides detailed information on various types of conduits and their corresponding fill capacities.
To make use of the Southwire Conduit Fill guide effectively, follow these steps:
- Identify the type and size of the conduit you plan to use.
- Determine the diameter of the wires you intend to install.
- Refer to the Southwire Conduit Fill guide for the corresponding conduit type and size.
- Follow the guidelines to calculate the maximum fill capacity expressed as a percentage.
The Southwire Conduit Fill guide is a valuable resource for accurate wire fill calculations, ensuring compliance and efficiency in electrical installations.
Efficient Wire Fill Calculation
To ensure efficient wire fill calculation, consider the following tips:
- Always refer to the appropriate conduit fill chart or calculator for accurate results.
- Consider the type of conduit, wire diameter, and ambient temperature when performing calculations.
- Double-check your calculations using multiple resources to ensure accuracy.
- Regularly update your knowledge of electrical codes and regulations to stay up-to-date with the latest requirements.
- Seek advice from experienced professionals or consult with manufacturers for complex installations or unique scenarios.
By allowing and following these tips, you can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your wire fill calculations, resulting in safe and reliable electrical installations.
Accurate wire fill calculation is essential for ensuring electrical installations' safety, efficiency, and compliance. By understanding conduit fill calculations and utilizing tools such as the Conduit Fill Calculator, Conduit Fill Chart, and other resources, you can simplify the process and achieve accurate results. Whether you're working with Cat 6 cables, specific conduit types, or seeking guidance from manufacturers like Southwire, the resources available can provide valuable insights and support for your wire fill calculations. Remember to stay updated with electrical codes and regulations and prioritize safety in your electrical installations.
CTA: For accurate wire fill calculations and to access valuable resources such as the Conduit Fill Calculator, Conduit Fill Chart, and Southwire Conduit Fill guide.
Why You Should Choose AC-DC Electric
If you’re still having trouble finding the right electrician to help you with your residential electrical issues, consider contacting AC-DC Electric. We maintain a network of reliable and affordable electricians who can offer assistance.
Our Experience
At AC-DC Electric, we have been offering both residential and commercial electrical services for over four decades. Our experience has taught us the best ways to perform various procedures.
Our management and staff have seen electric systems evolve over time and have gained a deeper understanding of how they work. Thanks to our experience, we rarely encounter issues that we have never seen before.
Our knowledge
Each of our electricians and technicians is licensed, certified, and trained to provide high quality services. We understand the importance that electric systems play in both residential and commercial properties. This is why we handpick the best staff who are both knowledgeable and have demonstrated their ability in a variety of situations.
At AC-DC Electric, we foster an environment that encourages excellence. You can count on our electricians and technicians to get the job done with both speed and skill.
Our Transparent Pricing
Dealing with an electrical problem at home can be incredibly distressing, and many electricians and companies are willing to exploit people experiencing such issues by charging them high fees. At AC-DC Electric, we strive to provide high quality services at affordable rates.
Our experts can also offer you a free estimate before you hire them. This ensures you remain aware of how much you will need to pay before using our services.
If you’re ready to tackle your residential property’s electrical problems quickly, please contact AC-DC Electric today. Our experts are always happy and ready to help residents in Fort Collins, Greeley, Evans, Johnstown & Windsor. Call today for a free estimate at 970-330-1656.
What is the maximum conduit fill percentage allowed by the NEC?
The NEC allows up to 53% fill for one conductor, 31% for two, and 40% for three or more conductors inside a conduit.
How many 12-gauge wires can fit inside ¾" EMT?
Typically 21 insulated 12 AWG THHN conductors fit inside ¾" EMT conduit.
Always verify using NEC Chapter 9, Table 4 & 5.
Do ground wires count toward conduit fill?
Yes. All conductors — including grounds — are included in the total area calculation.
Does conduit type affect wire fill capacity?
Yes. EMT, PVC, FMC, and rigid conduits have different internal diameters, which changes how many wires you can safely install.
Do bends in a conduit reduce allowable fill?
Bends don’t reduce fill, but they increase pull tension, which often requires upsizing conduit.
Can I mix wire gauges inside a single conduit?
Yes, but you must calculate the total combined area of all wire sizes. Mixing gauges increases complexity.
What happens if a conduit is overfilled?
Overfilled conduit can cause overheating, insulation damage, failed inspections, wire pulling difficulty, and electrical hazards.
Does EMT conduit allow more wires than PVC?
Usually yes, because EMT has a thinner wall, giving it a larger internal diameter compared to the same trade-size PVC.
Is flexible metal conduit (FMC) worse for conduit fill?
FMC has more friction and often requires upsizing. While fill rules apply normally, pulling difficulty increases.
Can I put NM-B Romex inside a conduit?
It’s not recommended except for short protection sleeves. NM cable insulation isn’t designed for full conduit runs due to heat buildup.
Do bends reduce the number of wires allowed?
No—bends don’t change fill percentage, but they increase pull friction, often requiring larger conduit.
How many bends are allowed between pull points?
The NEC allows a maximum of 360° of bends between pull points.
Does conduit length affect wire fill?
No, but long conduit runs increase pulling tension, making upsizing advisable.
Should I oversize conduit even if I meet the minimum fill requirement?
Yes. Electricians typically oversize by one trade size to allow easier pulls and future expansion.
Do all insulated wires have the same area?
No. THHN, XHHW, NM, UF-B, and TC cables all have different diameters and insulation thicknesses.
What is the formula for conduit fill calculation?
Fill % = (Total Wire Area ÷ Conduit Area) × 100
Where do I find official NEC conduit area tables?
NEC Chapter 9, Table 4 lists conduit areas.
Table 5 lists wire areas.
Are multi-conductor cables calculated differently?
Yes. Multi-conductor cables have one single combined area, found in manufacturer datasheets.
How do I calculate fill for control, fire alarm, or low-voltage wiring?
Follow the same area-based calculation, but low-voltage wiring often uses separate raceways for interference reasons.
What is the 40% rule?
For three or more conductors, your conduit’s total fill must not exceed 40% of its internal area.
Why is it so hard to pull wires through my conduit?
Possible reasons:
Too many bends
High friction (especially in FMC)
Overfilled conduit
No pulling lubricant used
Conductors are too large for the raceway
Can I add more wires to an existing conduit?
Yes, as long as the new total fill remains ≤ 40%.
Should I replace or enlarge the conduit if I add a new circuit?
Usually yes. Upsizing is safer and makes pulling easier.
Can homeowners legally calculate conduit fill themselves?
Yes, but installations must still pass local inspection. For safety, consult or hire a licensed electrician.
What size conduit do I need for a 50-amp EV charger?
Most 50A EV chargers use 6 AWG conductors, which typically require ¾" to 1" EMT depending on the number of conductors and run complexity.
What size conduit for a subpanel feeder
t depends on wire gauge—common feeder sizes include 1"–1¼" EMT/PVC, but always calculate based on conductor area.
You might also like